[language-switcher]
As the injection molding industry moves toward 2026, it is at a critical point and a combination of technological innovation and high environmental needs face each other. This massive summary is based on the latest assessments of the market along with expert insights to examine the changing landscape from material advancements to workforce. Projections show that it has strong growth potential and the global market is likely to expand from around USD 304.4 billion in 2025 to USD 481.6 billion by 2035, at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.26%. This growth is driven by the demand from industries such as automotive, packaging and electronics, where the ability of injection molding to produce complex and high-volume parts efficiently is unmatched. However, challenges like sustainability mandates and labor shortages loom large and call for an improved ability of manufacturers to adapt.
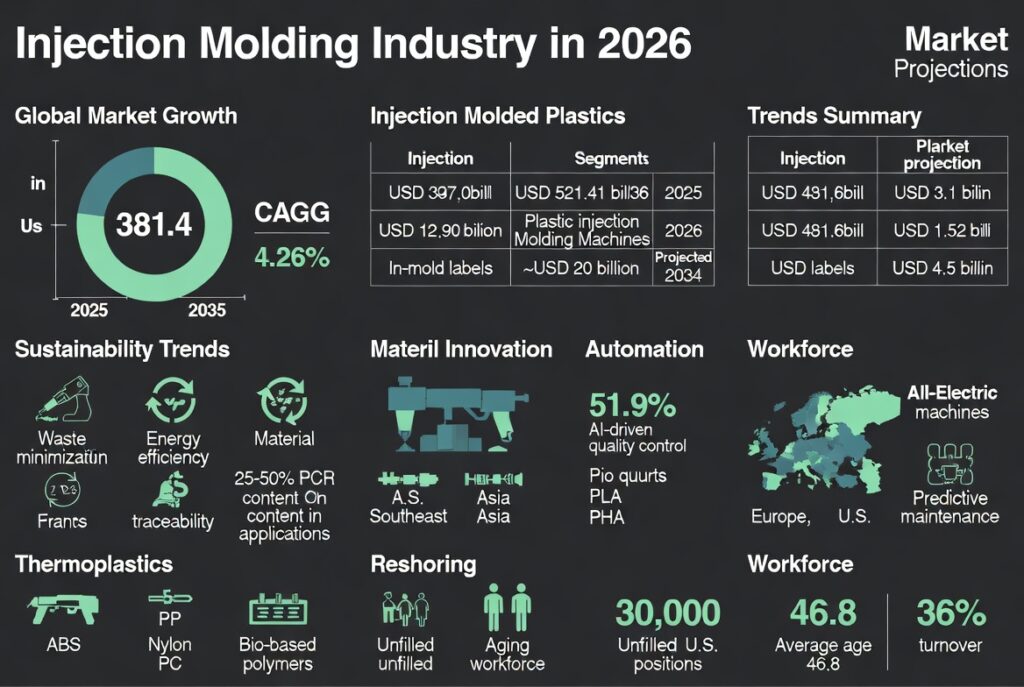
Sustainability becomes a cornerstone trend and is emerging as a trend from being niche to being an industry standard. By 2026, brands will increasingly make requirements for waste minimization, energy efficiency and traceability of the materials used for molded components. This is because of the growing regulations on single-use plastics and the corporate commitment to net-zero carbon goals. For example, usage of post-consumer recycled (PCR) content is expected to increase with blends reaching 25-50% in applicable uses with no major performance compromises. Bio-based plastics, which are made from a variety of sources such as corn starch or sugarcane, have a lower carbon footprint, but may come at the cost of toughness, so care must be placed in material choice. Mold designers are responding both by optimizing features, such as hot runners, to reduce scrap, by thinning the walls in order to save material, and by adding the ability to easily disassemble the mold for recycling.
In practice, this comes down to selecting durable parts with a lifetime up to 20 years, which may correspond to principles of circular economy with repairable and regenerable products. Challenges remain, however, especially in obtaining customer acceptance of recycled materials for high strata applications in which even relatively small levels of mechanical degradation may be unacceptable.
Materials innovation helps to complement these sustainability measures, and the dual focus is on eco-friendly alternatives and high-performance alternatives. Thermoplastics still dominate and account for more than 90% of molding materials, including staples such as ABS ($2.00-$4.00/kg), Polypropylene (PP) ($1.50-$3.00/kg), Nylon (PA 6/66) ($3.00-$5.00/kg) and Polycarbonate (PC) ($4.00-$7.00/kg). High end resins such as the PEEK or PEI are gaining ground as they are superior in heat/chemical resistance, ideal for automotive and aerospace applications. Bio-based polymers such as PLA and PHA are expected to drive rapidly, through 2029, especially in packaging and in agri tech, but their adoption for automotive and appliances is still moderated by such considerations as lightweight and gaining efficiency, rather than outright replacement of fossil fuels.

Co-design processes are important here in translating part specifications – functionality, exposure to the environment, production volume and aesthetics – into the best polymer and mold choices. Additionally, in-mold labeling is also set for expansion with the market developing from USD 3.1 billion in 2026 to USD 4.5 billion by 2033, due to the large volume of demand for durable, aesthetic packaging in consumer goods.
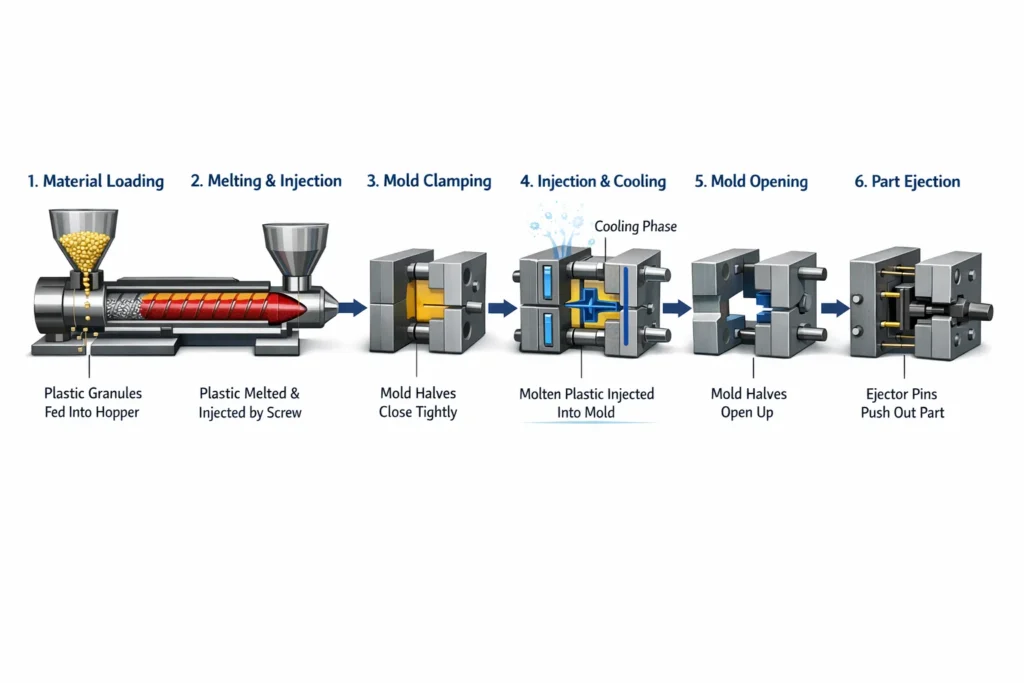
Automation and Industry 4.0 technologies are reshaping the production floor, which promises an improved level of precision and less downtime. And by 2026 integrated cells will do more than just injection: inspection, assembly and marking processes will be integrated, with in-line quality controls allowing for real-time adjustments. AI-driven systems will be able to detect minor defects – surface imperfections, colour variances, or dimensional inaccuracies – beyond the abilities of humans and provide consistency to operations. All-electric ones, expected to have more than 51.9% market share by 2035, can provide 50% energy savings and better accuracy compared to hydraulic ones. Hybrid variants are the best of both; and predictive maintenance through IoT ensures minimum disruptions. However automation is utilized judiciously to take over repetitive or key tasks and jobs are still retained for skilled operators such as setup and troubleshooting. This evolution continues up to sophisticated techniques such as overmoulding of Multifunctional assembly and insert moulding to embed metal or plastic components in one step. Integration with 3D Printing further speeds up the prototyping to make molds inserts to reduce the lead time.
Reshoring and diversification of supply chain are differentiated strategies of dealing with geopolitical uncertainties and post-pandemic vulnerabilities. Manufacturers increasingly localize their production in Europe and the U.S. to reduce lead times, improve quality control and to reduce the risks of overseas dependencies. As Jonas Persson, who is involved in key ways with the work in Rosti, says: “We’re seeing more customers reshoring, especially moving operations closer to their home markets both in Europe and the United States.” There’s a heavy focus on diversification of supply chain whilst also localization of production.” This includes expansion into Southeast Asia, new facilities in Vietnam and India to work around trade barriers and support growth in high potential sectors such as electric vehicles (EV). North America holds market dominance, but Asia-Pacific is expected to follow the same with the fastest CAGR, due to industrialization and tech adoption. These changes not only stabilise supply, they encourage jobs for the plastics sector also.
Workforce dynamics are a critical challenge – with more than 30,000 unfilled positions in the US alone – process technicians and automation engineers included. The aging workforce — it averages 46.8 years old, with one-third of the workforce over 50 years old — and a 36% turnover rate contributes to shortages. Younger generations tend to overlook manufacturing because of the perception of limited growth and increasing wages (11.3% increase in hourly rates, up to 18% for skilled roles). Upskilling is critical as automation brings with it hybrid roles that demand qualifications in robotics, PLC programming and data analysis. Solutions include internal academies, apprenticeships with organizations such as the Society of Plastics Engineers and rebranding efforts through social media to promote the high labor settings and sustainable appeal of the industry. Without these, production delays and overtime costs could work against you in being competitive.
Looking into the future, events such as the Plastics Technology Expo (PTXPO) 2026 will be able to display such innovations as networking and technology demo hubs. Market segments display different lines of development: the projected value of the injection molding machine market is USD 38.7 billion in 2026 versus USD 13.52 billion for plastic injection molding machines in the same year and increasing to other amounts in 2034. Overall, the industry needs to find a way to balance innovation and practicality in how data is used to optimize processes and to gain traceability in order to comply with audits and improve efficiency.
Market Projections Table
| Segment | 2025 Value (USD Billion) | 2026 Value (USD Billion) | Projected 2033-2035 Value (USD Billion) | CAGR (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Global Injection Molding Market | 304.4 | N/A | 481.6 (2035) | 4.26 |
| Injection Molded Plastics | 387.0 | N/A | 521.41 (2033) | ~3.8 |
| Plastic Injection Molding Machines | 12.90 | 13.52 | ~20 (2034 est.) | ~4.5 |
| In-Mold Labels | N/A | 3.1 | 4.5 (2033) | ~5.5 |
| Injection Molding Machines | N/A | 38.7 | N/A | N/A |
Trends Summary Table
| Trend | Key Drivers | Challenges | Opportunities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sustainability | Regulations, client demands | Material performance trade-offs | Circular designs, PCR blends |
| Materials Innovation | EV and packaging growth | Adoption barriers for bio-based | High-performance resins |
| Automation | Efficiency, precision | Upskilling needs | AI integration, energy savings |
| Reshoring | Supply chain stability | Regional labor variances | Expansion in Asia |
| Workforce | Tech evolution | Shortages, turnover | Training programs, rebranding |
In summary, 2026 promises to be an exciting time for injection molding and the convergence of sustainability and technology to fuel resilience and growth. Manufacturers that invest in these areas will not only be in compliance with evolving standards but also seize emerging markets ensuring long term viability in a competitive global arena.