An Overview of the Use of Plastic Products
We need to look at how the polymer pellets are produced to understand the full life cycle of the process. It is at the stage of production that the overall process of injection molding starts. In this stage, raw materials from the earth are transformed into polymers with the help of energy which is added to them. Compounders combine raw polymers with additives in order to give them the necessary properties to be used in applications, which are then added to the polymers in bulk.
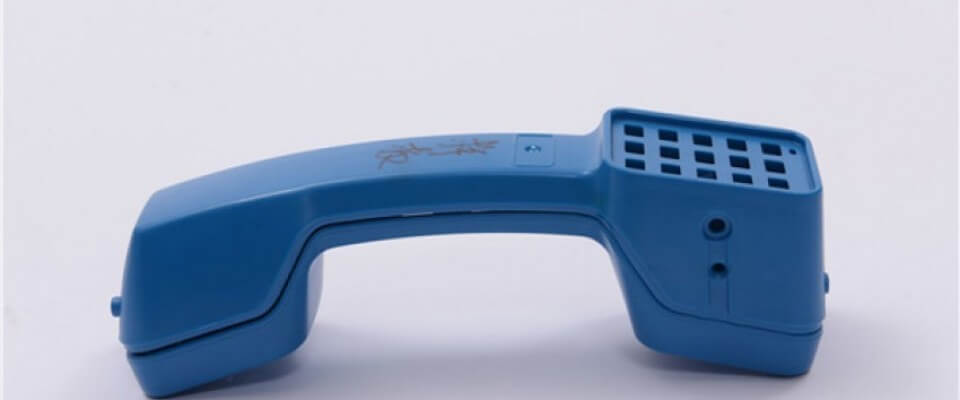
The polymer is sent to the injection molder for it to be transformed into final products by the injection molding process. Some additional additives, for example colorants, might be added to the product by the injection molding company. Injection molded products are ready for sale after they have been assembled and packaged to their final destination. There are large energy costs associated with the production of the materials for the injection molding process, particularly since a substantial amount of petroleum is used for the production of the polymer resins.
A large concentration of additives added to the base polymer can constitute a hazard in large quantities. By-products of this process are likely to be hazardous and not biodegradable, which is one of the biggest drawbacks of the process.
Plastics injection molding’s environmental impact
Plastic life cycle analysis must consider polymer production emissions because they are a major contributor to waste emissions. Emissions from the energy sector and those from the processing sector can be divided into two categories. In comparison with energy-related emissions, the site has few processing emissions. Landfills cannot decompose plastics.
The use of two different solutions has been observed over the last few years. The first option is to burn the plastic, which releases toxic materials into the atmosphere. The main reason for the widespread use of this method is the high heating properties of plastics, which are petroleum-derived. Japan and England are limiting how much petroleum-based waste can be disposed of at an incineration plant and promoting methods that recycle waste.
Because of this trend, it has become essential to include recycled plastic as part of the design phase, as well as the right blend of polymer material and additives to make products perform as effectively as possible. A second method entails recycling plastic and repurposing it for other purposes. Neither of these two solutions can be used for both types of plastic.
In the case of defects in a product or at the end of its lifespan, thermoplastics can be melted, while thermoset plastics cannot be melted. Automobiles are one of the areas where plastic can be recycled widely. Currently, U.S. car recycling methods rely solely on reusing metals. Waste plastic goes to landfills as scrap.
The energy consumption of injection molding is similar to that of other conventional manufacturing processes. Similar energy requirements are required by sand casting and die casting, for example (12-16.5 MJ/kg). Nevertheless, injection molding’s impact seems significant when compared to semi*conductor processes. To understand this point, however, we have to examine the product’s widespread impact on the economy as a whole. Some developing countries are embracing injection-molding processes more and more.
Although little waste material is generated in the process and the amount of coolant used is low, the amount of energy used has led to the development of ways to make the process more environmentally friendly. Efficiencies must be improved to reduce environmental impacts. An energy-saving process is essential, especially during this period of rising energy prices.