what is Real Cost of Injection Molding: A Complete Guide
Injection molding provides a production cost range from $1 to $5 per unit at high production volumes (10000 pcs per batch),and its initial mold costs start from $2,000 to $20,000. The production technique enables both high quality and economical mass manufacturing capabilities.
Injection Molding Cost Calculator
Estimate mold tooling cost and per-unit price for ABS, PC, PP, Nylon, POM plastic injection molded parts
INJECTION MOLDING COST CALCULATOR
Estimate mold tooling + unit price · Final quotation requires DFM review
Key Cost Components:
- According to research mold design together with creation expenses account for between 60-70% of startup expenses. The new technology from our company enhances mold production which cuts down initial capital expenses by 15%.
- Unit costs vary by 30-40% based on the selection of materials according to Material Selection and Cost Testing data. Our up-to-date data system optimizes material consumption which leads to a minimum waste reduction of 12%.
- Our Production Volume Analysis Studies show that manufacturing larger product quantities leads to lower unit price costs. The production of 100,000+ units enables cost reduction to under $1 per piece form some items.
Cost Comparison Table:
| Production Method | Initial Cost | Unit Cost (100k+) | Quality | Speed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Injection Molding | $3k-20k | $0.5-5 | High | Fast |
| 3D Printing | $0.8k-5k | $5-20 | Medium | Slow |
| CNC Machining | $1k-10k | $10-50 | High | Medium |
The market shows that injection molding expenses have reduced by 15% during the past five years because of technological enhancements and automated systems. The optimal production cost efficiency comes from running production at least 10,000 times according to expert analysis.
Injection molding is a really useful manufacturing method for making parts. It works by injecting melted stuff into a mold. The melted stuff can be metals, glasses, rubbers, or commonly something like plastic.
The way it works is, first the right material gets melted in a heated barrel. Then it gets injected at high pressure into the mold cavity, which is cooled. The material takes the shape of the cavity as it hardens, while the sprues and gates get removed from the part.
- China Plastic Mold and Injection Molding Cost
- history of injection molding
- cost of plastic mold
- cost of injection molding
- tips to reduce injection molding cost
- Consider opting for soft tooling
- Use a more efficient plastic resin
- Simplify Your Design
- Design More Efficient,longer-lasting and possible multi-cavity molds
- Reduce The Cycle Time
- Automate repetitive tasks and processes
- Utilize Parts Or Models Which Are Already Available
- Build New Models That Are Male Shaped
- Adopt Flat Runs-Outs
- Choose Supporting Structures Wisely
- Fillers Added
- Reduce Scrap
Injection molding is one of the most popular ways to make plastic parts because it’s fast, efficient, and really versatile. Injection molded stuff can range a lot in size and complexity, and gets used in tons of industries from medical to cars.
history of injection molding
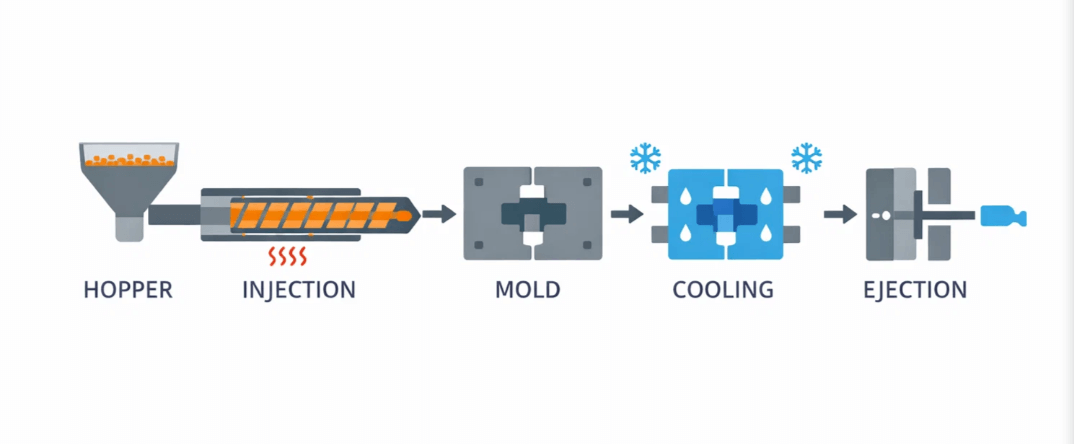
Injection molding is a great manufacturing process for making parts by squirting melted material into a mold. It was invented back in 1872 by this German engineer dude named Arthur Eichengrün. Eichengrün was a German engineer working on a way to make metal parts using heat and pressure. He figured out he could inject melted material into a mold and it would cool and harden quickly.It started getting used a whole lot in the 1970s. Injection molding is used to make all kinds of products, from medical gadgets to toys.
Eichengrün’s invention changed manufacturing, since it allowed mass production of parts with complex shapes. Injection molding quickly got popular in a bunch of industries, including cars.
Lots of people who purchase injection molds from China just care about saving money. But that’s not the right attitude, since you really want a mold that works right and is reliable instead of just being cheap.
cost of plastic mold
Plane size affects plate size, machining time, mold base standard, and often the required injection machine tonnage.
Depth changes core length, cooling layout, ejection stability, and the risk of deflection and warpage.
Undercuts typically add slides/lifters, precision fits, extra steel, and more assembly time—often a top cost driver.
More cavities increase machining + balancing + QC demands, but reduce cost per part at volume.
Steel selection impacts cost, polishability, corrosion resistance, and lifetime cycles.
Hot runners raise mold cost but reduce scrap and improve process stability for many parts.
Cosmetic and high-gloss surfaces add polishing time, tighter handling, and stricter tool marks control.
- Mold base + core/cavity steel selection
- Slides/lifters complexity (undercuts)
- Runner system choice (cold vs hot)
- Surface level (standard / cosmetic / high gloss)
- Multi-cavity scaling effect
Select inputs to generate an estimated range and a short explanation here.
Injection molding is one way used to manufacture plastic parts at scale. Its ability to deliver consistent, high-quality components at high speed ,which makes it ideal for mass production. However, injection molding is not without cost. Tooling and part prices are influenced by multiple factors, including resin selection, part size, design complexity, and production volume.
When these factors are carefully evaluated, sourcing injection molding tooling from China can be a cost-effective strategy—provided key considerations are addressed early in the project.
mold cost breakdown
| Item | Percentage | |
| 1 | Steel Material | 20-35% |
| 2 | Machining(CNC,engraving) | 25-40% |
| 3 | Assembly(bench work) | 15-20% |
| 4 | Mold design | 5-10% |
| 5 | Tax, profit | 20-30% |
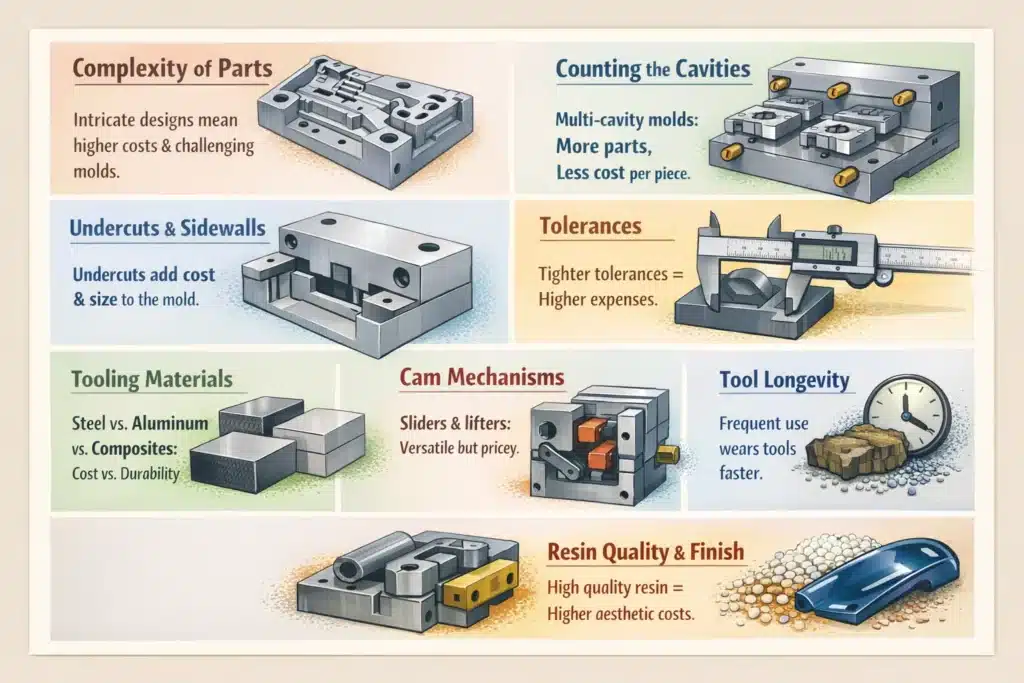
To determine How much a plastic mold tool and injection molding, some factors are considered:
Complexity of Parts:
As part geometry becomes more complex, mold construction difficulty increases accordingly. Fine details, thin walls, and complex features make it harder to ensure proper plastic flow and consistent part quality.
Even a single side-wall undercut can significantly increase tooling cost. Adding sliders or lifters typically adds USD 500 or more, while also increasing mold size and often requiring additional heat treatment.
Counting the Cavities:
Multi-cavity molds can significantly reduce per-part cost by producing multiple parts in one molding cycle. Depending on part size and volume requirements, a single mold may contain two, four, or even more cavities.
While multi-cavity molds cost more upfront, they often result in lower cost per part for medium- to high-volume production.
Narrowing Down Tolerances:
Tight tolerances directly increase tooling cost. Achieving narrow tolerances requires higher-precision machining, better steel, more polishing, and stricter process control.
A practical approach is to apply tight tolerances only where functionally required, while allowing looser tolerances elsewhere to control tooling cost.
Choice of Tooling Materials:
- Steel molds (P20, 718, H13, S136) offer long tool life and dimensional stability but come at a higher cost.
- Aluminum molds are less expensive and offer excellent thermal conductivity but wear faster.
- Composite materials (carbon fiber, fiberglass) provide moderate durability at lower cost but are generally unsuitable for high-volume production.
Material selection should align with expected production volume and part performance requirements.
Unveiling Cam Mechanisms:
Cam mechanisms such as slides, lifters, and unscrewing systems enable complex geometries but add both cost and risk. These components increase machining time, assembly labor, and long-term maintenance requirements.
Tool Longevity:
Tool life depends on:
- Resin type (filled vs unfilled)
- Production volume
- Operating conditions
- Maintenance practices
A higher-cost mold used in high-volume production often delivers lower cost per part over its lifetime compared to a cheaper mold with limited durability.
Resin Quality and Aesthetics:
Higher-grade resins and cosmetic surface finishes require:
- Better steel quality
- Higher polish levels
- Tighter process control
Tooling Type vs Part Cost
While hot-runner molds are more expensive than traditional two-plate molds, they eliminate runner waste and reduce labor costs. Over high volumes, this often results in lower per-part cost, despite higher initial tooling investment.
Why Tooling Should Not Be Purchased by Price Alone
Purchasing teams should not independently decide on mold specifications. Tooling decisions require input from:
- Mold designers
- Manufacturing engineers
- Production and quality teams
The objective is not the cheapest mold, but the lowest-cost mold that reliably produces parts to specification.
Information Required for an Accurate Tooling Quote
To obtain a reliable tooling quote, buyers should provide:
- 2D drawings and 3D CAD files
- Material (resin) specification
- Required tolerances
- Surface finish requirements
- Projected annual and lifetime volume
- Mold type (two-plate, three-plate, hot runner, etc.)
- Special mechanisms (slides, lifters, unscrewing)
- Part dimensions and projected area
- Sample part (if available)
Mold Design & Manufacturing Considerations
Mold builders must define:
- Number of cavities
- Cooling layout and line placement
- Ejection system
- Gating and runner design
- Mold base and standard components
Each manufacturing step should be timed and costed, including:
- CNC machining
- EDM
- Heat treatment
- Polishing and texturing
- Assembly and testing
Typical Tooling Timeline
A standard injection mold typically requires 4–10 weeks from design to T1 sampling, depending on complexity.
Using a supplier that offers both tooling and injection molding helps avoid delays and additional shipping costs.
Final Recommendations
- Engage mold builders early in product development
- Involve engineering, purchasing, and management in cost decisions
- Get detailed, itemized tooling quotes
- Focus on total cost of ownership, not just initial mold price
With proper planning, higher initial tooling investment often leads to lower per-part cost and better long-term profitability.
cost of injection molding
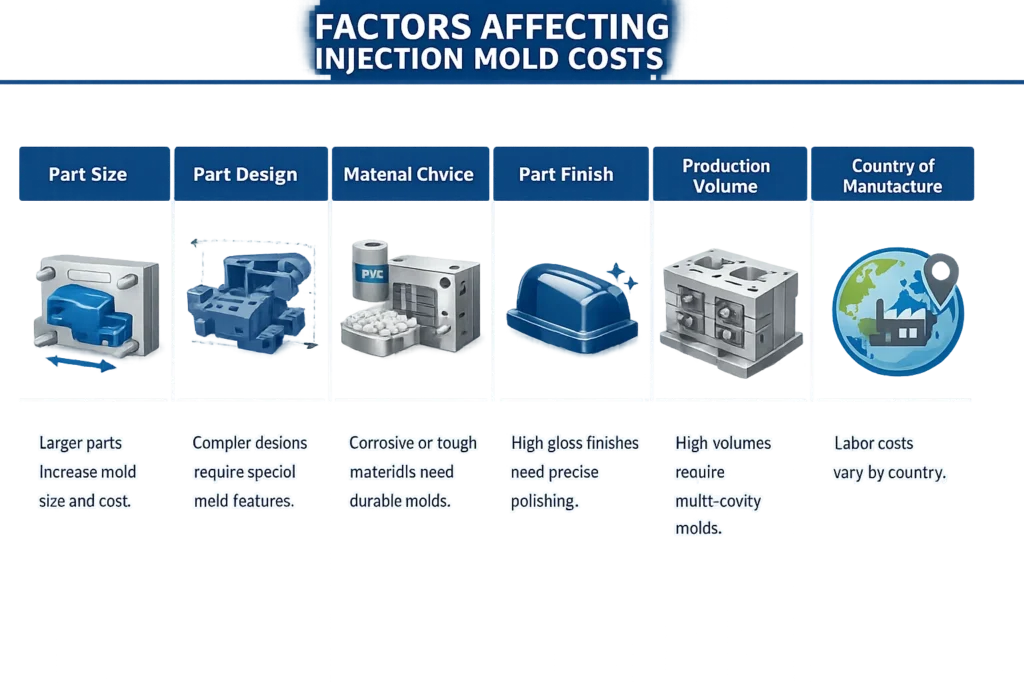
The cost of injection molding will depend on a number of factors, including the size and complexity of your part, the type of plastic being used, and the quantity being made. In general, it costs more to manufacture small quantities than large quantities.
Why those important for injection molding cost
- Part size- bigger parts mean a bigger mold, which means that bigger steel will increase the steel cost for the injection mold.
- Part design- the more complex a part is, the more detailed the mold has to be. Some complicated parts will require special features to be added, such as lifters or sliders. Therefore, you should be open to advice from your mold maker and see if there’s anywhere that you can alter the part design to save on injection mold costs.
- Materials: Depending on the part material of choice, the injection mold will have to be made of a particular material. For instance, if corrosive plastic-like PVC is to be used, the mold will have to be stainless steel to avoid any damage, ultimately bump the price up.
- Part finish requirements- where parts have high gloss surface requirements, then more expensive steel and precise technical polishing will be vital, adding to the price.
- Production volume- higher volume molds need more cavities, and so the mold will be larger. They also require a higher steel grade to last for longer, which impacts the injection mold cost.
- Country of manufacture- different countries have different wage rates. If your mold is made in a country where labor costs are low, then you’ll naturally save money. In China, the average cost of an injection mold is around 40% less than in western nations.
tips to reduce injection molding cost
Practical Ways to Reduce Injection Molding Costs
Below are proven strategies to help keep injection molding costs as low as possible without compromising quality or performance.
Consider Soft Tooling Where Appropriate
Soft tooling is a cost-effective alternative to traditional hard tooling made from steel or aluminum. It typically uses materials such as polyurethane or other flexible compounds, which are less expensive and faster to produce.
This approach is especially suitable for low-volume production, prototyping, and early-stage product development. Soft tooling also offers greater design flexibility and significantly shorter lead times, making it an attractive option for companies with limited injection molding experience or evolving design requirements.
Select Plastic Resins Strategically
Material selection plays a critical role in controlling injection molding costs. Different resins are designed for different production volumes and performance requirements, and choosing the right one can significantly reduce expenses.
Cost savings can also be achieved by:
- Using resins that require less energy during melting and cooling
- Incorporating recycled plastics where feasible
- Selecting materials compatible with simpler tooling and faster cycle times
For example, replacing thick-walled rigid PVC parts with materials such as ABS or polypropylene (PP) can reduce energy consumption due to their thinner wall designs and more efficient thermal behavior.
Simplify Part and Mold Design
Highly detailed CAD drawings are not always necessary during early design stages. A basic sketch with clear descriptions and a part print can often suffice, reducing engineering time and CAD-related costs.
Design complexity has a direct impact on manufacturing cost. Parts with intricate geometries require more sophisticated tooling, longer production times, and higher material usage. Likewise, excessive wall thickness increases material consumption and cycle time, driving up costs.
Keeping designs simple and functional is one of the most effective ways to reduce both tooling and per-part expenses.
Design Efficient, Durable, and Multi-Cavity Molds
Injection molds naturally wear over time, especially under high pressure and temperature. Designing molds for durability can significantly reduce long-term costs. This includes:
- Selecting materials with appropriate wear resistance (e.g., aluminum for lower volumes, steel for high-volume runs)
- Using advanced alloys such as titanium or nickel for high-stress components
- Avoiding unnecessary mold complexity
If multiple identical parts are required, a multi-cavity mold can greatly improve productivity and reduce per-unit cost compared to single-cavity molds.
Reduce Cycle Time
Cycle time includes all steps required to produce one part:
- Material feeding
- Melting and injection
- Cooling and solidification
- Mold opening and part ejection
Shorter cycle times allow more parts to be produced in less time, lowering unit costs. Optimizing cooling, wall thickness, and mold design can dramatically improve cycle efficiency.
Automate Repetitive Operations
Automation reduces labor costs, increases consistency, and minimizes downtime between cycles. Automated systems can also shorten cycle times and reduce workplace injuries caused by repetitive tasks.
While automation requires an initial investment, it often delivers strong long-term cost savings and improved production reliability.
Reuse Existing Parts or Models
Plastics are inherently well-suited for replication. Using existing parts, prototypes, or proven models as references can significantly shorten development time and reduce design costs.
Build Male-Shaped Master Models
When creating master models, male-shaped designs are typically easier and faster to duplicate. Using minimal metal thickness further reduces material and machining costs.
Favor Simple Structural Features
Maximizing flat run-outs and avoiding unnecessary contours simplifies tooling and improves manufacturing efficiency. Simple geometries are easier to mold, inspect, and maintain.
Choose Support Structures Carefully
Each support structure material has trade-offs:
- Wood: Lightweight and inexpensive, but dimensionally unstable
- Cast iron: Affordable but requires extensive machining
- Aluminum: Higher material cost, but faster to machine
- Cast steel: Strongest option, but most expensive and time-consuming
Selecting the right support structure can significantly impact overall project cost and lead time.
Use Fillers to Reduce Material Costs
Fillers can reduce material costs while enhancing hardness and stiffness where high strength is not required. Common fillers include clay, calcium carbonate, limestone, and aluminum oxide. These additives are especially useful in large or durable plastic components.
Minimize Scrap and Defects
Scrap is a major cost driver in injection molding. Poor quality control leads to rework, delays, and wasted materials. Implementing effective inspection systems—such as laser or automated inspection—can identify defects early and significantly reduce scrap rates.
Final Thoughts
While partnering with a reliable injection molding supplier is essential, cost control ultimately depends on smart design decisions, material selection, efficient tooling, and optimized processes. Applying these strategies holistically can substantially improve profitability and long-term manufacturing efficiency.