If you want to find a quality injection molding factory in China, you need to complete the entire journey of the inquiry, risk management, proofing, the entire process of the molding, manufacturing, and delivery to mass production.
China has been dominating the injection molding manufacturing industry for the past ten years. Realistically, “China injection molding supplier” seems easy to find, however, the quote “really reliable and suitable supplier for you” is an arduous task.
This guide was created from the industry, internal supply chain management, mold making technical specifications, and years of procurement.
This guide has 50+ selection criteria, 33 risk points, a full decision tree, templates, and industry case studies from the USA and Europe.
This guide will allow you to:
- Tell the good from the bad for suppliers
- Tell if the offering is genuine or perhaps a ploy to get you in a low pricing trap
- Pick the best supplier group based on your expected product from them and quantity
- Steer clear of the mold, the resource fraud, mass production, and other regular industry fails
- Us custom templates to run audits on suppliers based on a set checklist
- Create an available “Chinese injection molding supplier selection system” for your company.
Let us begin.
Part 1 — Why Choosing the Right China Injection Molding Supplier Is So Difficult
Selecting a China-based injection molding supplier should be simple. You compare price, look at a few samples, ask a friend, check Alibaba, and place the order.
But reality is very different.
In the actual operation of China’s supply chain, “choosing the right injection molding supplier” is the most critical step in determining the success rate, yield, delivery time, and final profit of the project. This section will explain in depth:
- Why do companies always fall into traps?
- Why do seemingly established suppliers also overturn?
- Why the lowest-priced option could become the most expensive version?
- Why overseas buyers are more likely to be misled by factories than local buyers
- Why “injection molding difficulty” is grossly underestimated
Let’s start with the most common questions.
1. The most common pain points when looking for Chinese injection molding suppliers
You have most likely experienced each of the following:
1.1 never see the real factory capabilities
Most Chinese injection molding factories will not say:
- “We don’t have the experience to make products of your level”
- “Our mold capabilities are not enough”
- “The reason we quote a low price is because we don’t know how high the accuracy you require”
- “We have never made medical-grade transparent parts”
- “We cannot control the tolerance to±0.02mm”
Instead they will say::
“We can do. No problem. Very easy.”
WHY?
Because in Chinese factory culture:
- Will not reject customers easily
- Afraid of losing orders
- Confidence or blind optimism
- I think the problem can be solved later
- Unsure of the customer’s true requirements
The end result is: you simply can’t tell from the first round of communication whether the factory really understands your product.
1.2 Overseas buyers don’t understand the real difference in “mold quality”
Many foreign companies think that “a mold is a mold.”
But in reality:
| mold gade | allplication | life(shots) | accuracy | price difference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | easy shell,toy | <50k | low | cheap |
| L2 | ndustrial parts, general consumer goods | 100k–300k | medium | medium |
| L3 | Auto parts, structural parts | >500k | high | high |
| L4 | Medical, transparent parts, precision part | >1M | very high | very high |
Many failure cases occur when: Buyers need L3 ,but the factory does it according to L1 .Because you don’t understand injection molding industry. The factory will not tell you the real difference,maybe they didn’t know at all.
You thought you made a very good deal, but in fact you bought a “cheap but worthless mold.”
1.3 The factory will not tell you: your product is actually “difficult to make”
Do you think this is just a simple plastic piece?
Maybe the factory is thinking:
- “The mold needs extra sliders or lifters due to this undercuts or side holes.”
- “The wall thickness is so thin that the section will be hard to fill”
- “The thick section parts will deform without enough cooling water channels.”
- “The tolerance is so strict, we can’t do it”
- “This product is defective in design”
but they won’t say
Because:
- afraid you won’t place an order at my factory
- We can solve it later
- Maybe really don’t know how difficult it is (more dangerous)
Eventually you will find:
- Can’t make a sample
- Made but so many problems
- Many NG
- cannot be assembled
- Actual cost 2–3 times higher than quoted price
1.4 Delivery delays and quality disasters due to “low price trap”
This is the most common pitfall for foreign buyers:
- Quotes are 30–50% lower
- You thought you made a good deal In fact, the factory simply cannot make high-quality molds with this budget. So they change low grade steel and use low quality plastic material.
The result is:
- Mold life is 1/5 from the original quotation.
- Batch failed rate 10–40%
- Slow Production (poor cooling design)
- Modifications are done every month
- Every mass production need to be reworked
- The project will never be stable
Eventually you find:
The lowest offer is often the most expensive one
1.5 constantly “misunderstood” dut to Remote communication
What Chinese injection molding factories are good at is:
- CAD drawing
- Traditional processing requirements
- Simple structural requirements
However, overseas customer requirements may include:
- International testing standards
- UL certification
- UV resistance
- Assembly tolerance stack-up
- Structural requirements for future expansion
- Supply chain risk end user experience
These are almost always ignored in the first round of communication
lead to:
- wrong-design modification- mold modification-1-4 months delay.
- Or the product never meet its original standards.
1.6 Real situation emerged after months
Nearly all buyers have the following experience:
- Month 1: Everything ok
- Month 2: Sample little problem
- Month 3: You have your design problem.
You do not know until half-way through the project:
- the factory machinery outdated.
- The number of technicians is not enough.
- You are not their VIP.
- They have too many low-priced orders.
- No professional project manager .
- Nobody knows much of your parts.
- The part is subcontracted to other plants (you do not know).
Now it is too late for you to change factories.
2. It is not merely a factory you want, but the “appropriate factory.“
What is not actually understood by the overseas companies is that:
China’s injection molding factories fall into 5 entirely distinct categories based on capability, scale, and positioning.Choosing the wrong type = an 80% probability of project failure.
Below are the most common types found in the market:
| Type | Scale / Setup | Capabilities & Traits | Pros | Cons / Risks | Best For | Not For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small-Scale (cheapest, least reliable) | 10–20 workers; 4–12 outdated injection molding machines; no mold flow analysis; no engineers | Extremely low quotes; suitable for toys, small housings, low-precision parts | Lowest cost | No quality management system; no professional project management; frequent delivery delays | Low-budget, small-batch parts | Structural parts, transparent parts, precision parts |
| Mid-Sized | 20–100 injection molding machines; complete engineering team; in-house mold design capability | produce most industrial parts and consumer electronics components | Broad capabilities; generally stable | Large variance in capability and quality; needs careful supplier evaluation | About 90% of overseas buyers | — |
| Integrated Mold Shop + Molding (best overall) | Strong in structural optimization; capable of complex molds; can anticipate risks; stable mass production | Excellent for tight tolerances, undercuts, thin walls, complex structures, high cosmetic requirements | End-to-end control; strong risk management; consistent mass production | Typically higher price than standard mid-sized shops | High-requirement products and volume production | |
| High-End Precision Mold Makers (auto/medical) | ±0.02 mm; transparent parts; PC optical parts; multi-cavity; complex hot runners | Top-tier precision and cosmetic control | Extremely stable quality | Higher pricing; stricter lead times and communication discipline | Automotive, medical, optics, high-precision parts | |
| Trading Companies (mixed results) | Strong English communication; project management; supplier screening | Acts as a bridge coordinating the supply chain | Better communication; smoother project progress | Higher total cost; the wrong trader can be worse | First-time buyers; teams lacking engineering or local supply-chain resources |
3. Major Disasters for Choosing the Wrong Supplier
Each of the following issues could cost your extra 3–9 months or even fail.
3.1 Mold Design Errors
Manifestations:
- Couldn’t release from mold
- Uneven cooling
- Very thin walls
- Excessively prominent ejector pin marks
- Shrinkage and deformation
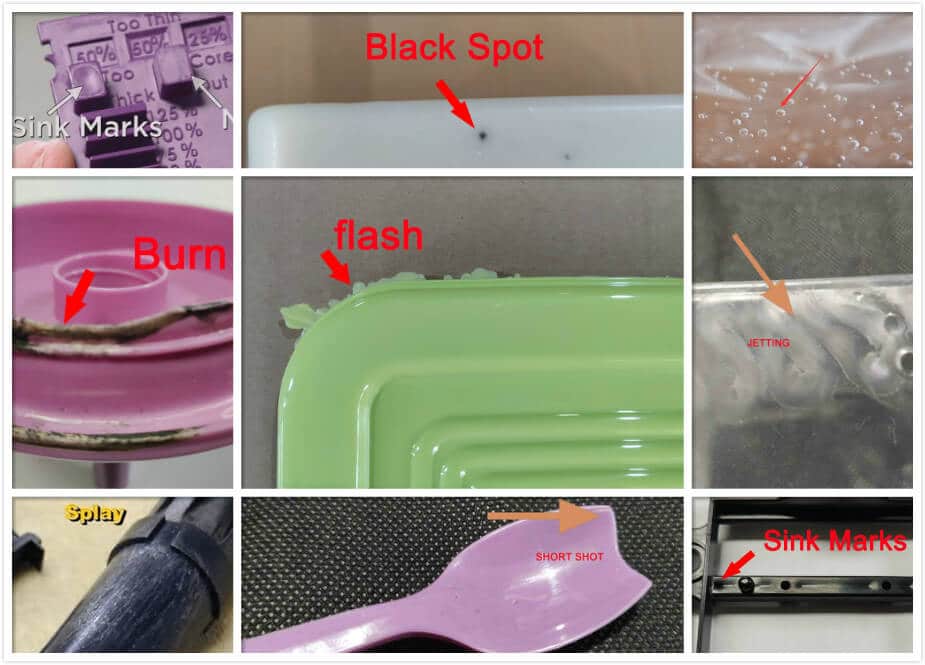

3.2 Wrong Material
Issues:
- recycled material
- lower-grade material
- No material brand
- Unstable coloring
Ultimate Consequences:
- Brittle fractures
- Finger print marks
- Discoloration
- Aging
❗Expanded Failure Cases
Case 1: Material Substitution
Tests were successfully completed on prototypes, and at the time of mass production, the supplier simply replaced PC with ABS to be able to match the schedule. Pictures were similar, but the impact tests were not successful and 2,000 sets were discarded. COA did not correspond with batch labels, and the supplier think it to be equivalent. Mold need to be reworked and customer delay fines were included in losses.
Case 2: Overstated Mold Life
Quote was 300k shots, defects began at about 80k flash and dimensional drift. Maintenance records were not full and they had to polish gates to make ends meet. We were experiencing biweekly line stoppages, our yield dropped to 92% and we also sub-docked orders to a backup factory, which added additional logistics and changeover expenses.
3.3 Mold Cost-Cutting
Includes:
- Reduced cooling channels
- Reduced ejector pins
- Non-compliant steel grades
- No heat treatment
- Low-cost hot runner systems
Resulting in:
- Shortened mold life
- Slow cycle speed
- High defect rates
- Increased mass production costs
3.4 Unstable Mass productoin Quality
Causes:
- Personal levels
- Outdated injection molding machines
- Non-standardized process parameters
- Poor raw material management
3.5 Inconsistent Quality Between Samples and Mass Production
Sample Production:
- New machines used
- Premium materials used
- Well Adjusted machines
Mass Production:
- Standard machines used
- Cheaper materials used
- Poorly adjusted machine
3.6 Suppliers Subcontract
Extremely Common:
- Insufficient in-house capacity
- Unable to handle complex structures
- Outsources low-cost processing for you
The factory you see ≠ the actual production facility.
3.7 Assembly Tolerance Issues
You assume the injection molding factory understands:
- Cumulative tolerances (stack-up)
- Assembly clearances
- Different material shrinkage
- Post-molding dimension change
But many factories lack this understanding entirely.
3.8 Lack of Project Management
Resulting in:
- Missed engineering drawings
- Unconfirmed tolerances
- Unconfirmed materials
- Unconfirmed structural details
- inaccurate delivery schedules
3.9 Poor Communication
Even basic instructions like:
- “Surface finish: MT11010”
- “Tolerance: ±0.05mm”
- “Requires food-grade material”
can be misinterpreted.
Summary: Chinese injection molding suppliers must be evaluated in a systematic approach. Instead of simply basing it on price, samples and reviews offered by Google or Alibaba, your selection criterion should be:
- Technical competence Experience in molds
- Alignment of the complexity of the structure
- Understanding of materials
- Project management skills
- Communication skills in engineering
- Quality control competence
- Transparency of the factory
- Potential of a sustainable partnership.
Part 2 — Evaluate China Injection Molding Suppliers
In the last part we discussed the pitfalls, low-price trap and why foreign purchasers would fall into trouble when selecting the injection molding suppliers in China.
Next comes the most imperative section, which is to develop a scientific and reproducible supplier evaluation system. This would allow you to easily decide on the reliability of a factory without losing money due to errors and defects.
1. Setting up a Supplier Selecting Process.
The procurement project, being highly complex, must rely on a five-step approach:
1. Initial Screening
- Sources: Alibaba, trade shows, referrals, overseas supply chain networks
- Qualification Verification: Business license, ISO/TS certificates, major client case studies
- Eliminate Clearly Unviable Suppliers
2. Capability Assessment
- Technical Capability: DFM (Design for Manufacturing), mold flow analysis, mold design, material handling
- Equipment Capability: Injection molding machine tonnage, CNC, EDM, CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine)
- Quality System: IQC (Incoming Quality Control), IPQC (In-Process Quality Control), FQC (Final Quality Control), OQC (Outgoing Quality Control), FAI (First Article Inspection), CPK (Process Capability Index)
3. Quotation Evaluation
- Breakdown of Mold Costs
- Breakdown of Injection Unit Prices
- Hidden Costs: Material markups, rework, logistics, communication delays
- Avoid Low-Price Traps
4. Sample Validation
- T1 Sample (Initial Version)
- T2 Sample (Revised After Feedback)
- Mass Production Trial (Small Batch Run)
5. Long-term Cooperation Potential Assessment
- Factory Response Speed
- Engineer Communication Skills
- Delivery Accuracy Rate
- Project Management Capability
- Risk Control Ability
- Willingness for Sustainable Cooperation
2. Initial Screening: How to Quickly Determine Factory Viability
Key Indicators:
| Indicator | Checking Method | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Company Qualification | Tianyancha / Alibaba / Exhibition Materials | Confirm the inclusion of injection molding and mold manufacturing in the business scope. |
| Years Established | Official Registration Information | Generally, a reliability of over 5 years is preferred. |
| Employee Count | On-site/Video | A plant with 50–500 employees is suitable for various production needs. |
| Injection Machine Tonnage | Video/Factory Materials | Ensure compatibility with your part structure and dimensions. |
| Mold Capability | Mold Cases, Mold Steel, Cavities | Check if they have made similar complex parts |
| ISO/TS Certification | Verify Certificate Authenticity | Be cautious of fake certificates; confirm authenticity on-site or via video |
Tip:The goal of the initial screening is not to find the perfect factory but to eliminate obviously unfeasible factories and narrow it down to 10–15 candidates.
3. Technical Capability Evaluation
3.1 Engineering Capabilities
- DFM Reports: Does the company present Design for Manufacturing (DFM) reports?
- Mold Flow Analysis: Does it carry out Moldflow Analysis?
- Optimization Skills: Do they have the ability to optimize wall thickness, draft angles, and parting lines?
- Complex Mold Experience: Do they deal with complex molds, hot runners, and slides?
- Material Knowledge: Do they know the properties of different plastics (e.g., PP, ABS, PC, PA66, POM)?
- Material Alternatives: Is it possible that they suggest alternative materials?
3.2 Mold Capabilities
- Steel Check: Can the grade of steel and the source be checked?
- Lifespan of Mold: Is the lifespan of the mold within the production requirements?
- Machining Precision: What is the precision and capability of EDM/CNC machining?
- Warranty Terms: What are the terms of warranty for the molds?
- Design Rationality: Does the design of hot runners, ejector pins, and venting make sense?
- Delivery Control: Does the mold delivery time make sense?
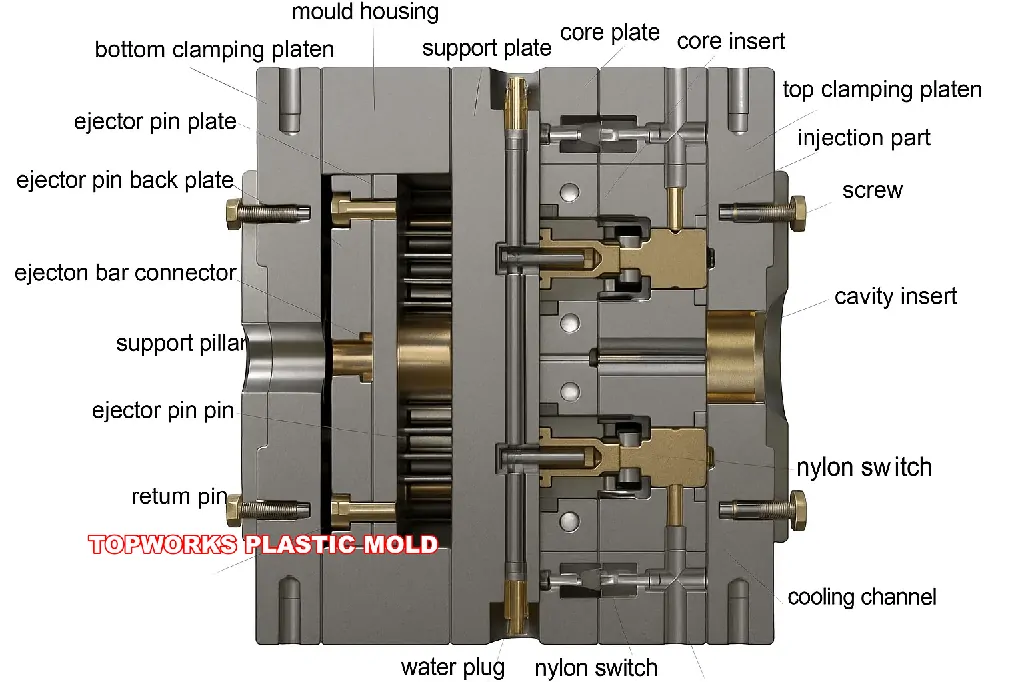
3.3 Equipment Capabilities
- Injection Machine Compatibility: Does the tonnage of the injection machine fit into the structural dimensions?
- Multi-Cavity Control: What is the issue with hot runner and multi-cavity mold control?
- Finishing Capabilities: What does it have in terms of polishing, spraying, silk screening, and assembly capabilities?
- Inspection Equipment: Does it have CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) and optical inspection equipment?
- Management Systems: How high is the MES (Manufacturing Execution System) and ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) management?
Recommendation
Video Assessment: The best way to assess is to carry out a video inspection and demonstration of the injection molding process of the factory. It is not enough to use pictures or brochures.
4. Quotation Evaluation: Visible Dissection and Escape Low-Pricing Traps
Quotation Breakdown Method
- Mold Cost = Steel + Mold base + CNC/EDM + design + assembly + profit.
- Unit Price = Material + Molding Cycle + Labor + Post Processing + Packaging + Defect rate Loss.
4.1 Hidden Costs
- Material Markup: This is used especially with transparent parts and engineering plastics.
- Mold Modification Fees: Extra expense would be paid on a change in the mold.
- Rework Costs: Costs to fix the mistakes.
- Logistics and Tariffs: Transport and custom fees.
- Communication Delays: Costs that are incurred due to a misconception or a problem in translation.
4.2 Avoiding Low-Price Traps
- Red flag: Quotations that are considerably less than those in the market (e.g., 30%) are dangerous.
- Quality Requirement: There could be some compromises in the mold steel or hot runner materials.
- Undercapacity of the Machine: A machine with inadequate power may result in more time-draining molding and increased variation of quality.
- Absence of Quality Control: No process of quality assurance will lead to high rates of rework.
Tip: When asking the suppliers to quote, always ask them to make a clear breakdown of quotation, such as specification of the steel grades, labor hours, and lifespan of the mold.
5. samples checking(T1 → T2 → Small Batch)
5.1 t1 Sample
- Dimensions: Verify that the molded parts meet the specified dimensions.
- Appearance: Assess the visual quality and finish of the parts.
- Shrinkage: Monitor any shrinkage that occurs during the cooling process.
- Warping: Check for any warping or distortion of the molded parts.
5.2 T2 sample
- Process: Modify the mold from the T1 sample checking result.
- Verification: check dimensions and functionality again.
5.3 Small Batch
- Confirm the stability of mass production.
- Defect rates
- Color accuracy
- Glossiness
Tip: Always conduct a small batch test of at least 50–200 pieces before mass production to ensure the factory’s ability to produce consistently.
6. Potential Long Term Collaboration.
Besides technical capabilities, the potential of long-term cooperation is also important. Evaluation and observation:
| Assessment | observation |
|---|---|
| response speed | Response time from Email, WeChat, Skype, WhatsApp. |
| Engineering Skills | Ability to understand complex designs and tolerance requirements |
| Delivery Accuracy | Check previous orders and small trial production |
| Project Management | Dedicated people to track the production processes |
| Risk Control | Changes in the moulds, material replenishment, and rework |
| Willingness for Long Time Cooperation | long-term collaboration, acceptance of NDA and mold ownership contracts |
Tip: Collaborating on a long-term basis is better than low prices in the short-term.
7. Understanding Technical Documents
1. Moldflow Analysis Report
Key Focus :
- Weld lines
- Shrink marks
- Bubble locations
- Cooling uniformity
Purpose: Assess the mold design reasonablity
2. DFM Report (Design for Manufacturing)
- Wall thickness
- Draft angles
- Radii
- Tolerance
Purpose: Evaluate production feasibility.
3. Sample Testing Report
Key Focus :
- Dimensional deviations
- Tolerances
- Material properties
- Surface finish
- Color
Purpose: Validate factory capabilities.
4. CMM Inspection Report (Coordinate Measuring Machine)
Key Focus :
- Critical dimensions
- Tolerance of mating holes
Purpose: Check mass production controllability.
8. Systematic Evaluation
Factory Questionnaire Example (Ready to Use)
- How many injection molding machines ? What is the clamping tonnage for each machine?
- What is your mold manufacturing capability? What types of steel do you use? What is the expected lifespan?
- Do you provide DFM or Moldflow analysis?
- Do you have IQC, IPQC, FQC, OQC, FAI, or CPK processes?
- What is the typical lead time for molds? How do you handle delays?
- Is there a limit on the number of sample modifications?
- Can you provide small batch trial production?
- Are you willing to sign an NDA?
- What are the terms regarding mold ownership contracts?
- Can you provide references or case studies from previous clients?
QC Inspection Checklist Example
- Appearance: Warping, bubbles, scratches
- Dimensions: Critical dimensions ± tolerances
- Materials: Color, glossiness, certifications
- Molds: Ejector marks, shrink marks, parting lines
- Batch Stability: Dimensions, weight, defect rates
Tip: By combining questionnaires and checklists, you can quickly compare multiple suppliers.
9. Scientific Supplier Evaluation Process
By implementing a scientific supplier evaluation process, you can:
Use structured criteria to identify and choose the supplier that best fits your specific needs and project requirements.
- Avoid Low-Price and Mold Traps
Prevent falling into the pitfalls of choosing suppliers solely based on low prices which may compromise quality.
- Validate Factory Technical Capabilities and Quality Systems
Ensure that the supplier has the necessary technical expertise and quality management systems in place to meet production requirements.
- Verify Mass Production Feasibility
Use small batch production runs to test and confirm that the supplier can meet your mass production needs effectively.
- Assess Long-Term Collaboration
Evaluate the supplier’s capability for long-term partnerships, including reliability, capacity, and willingness to adapt to changes.
- Select the Most Suitable Supplier
Use structured criteria to identify and choose the supplier that best fits your specific needs and project requirements.
Part 3 — China Injection MoldingCost Breakdown
In the previous sections, we talked about the problems with picking Chinese injection molding suppliers as well as how to methodically evaluate factories’ capabilities. Next, we move on to how to break down the costs of the molds and the costs related to injection molding, along with the hidden costs that are often disregarded. This will be essential to avoid price traps and the costs that come with having to redo the work with the additional time to be reimbursed.’
Injection Molding Cost Calculator
Instant Cost Estimation
1. Breakdown of Mold Costs (Transparency)
Many overseas purchasers focus just on the total price of the molds without understanding the internal components, and it makes them susceptible to misleading low prices or unreasonable quotes from suppliers.
1.1 Main Components of Mold Costs
| Cost Category | Percentage | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Steel | 20-35% | price differences amongst steels like P20, 718, H13; the quality impacts lifespan considerably. |
| Mold Base | 10-15% | Comes with the default mold bases and custom extra supports that will be added. |
| CNC / EDM | 25-35% | Milling, EDM, drilling, along with slide processing. |
| Design / Engineering | 5-10% | DFM, mold flow analysis, optimization of ejector pins and parting lines |
| Assembly / Polishing / Debugging | 10-15% | Setup of the machine, test runs, smoothing treatments, and hot runner debugging. |
| Hot Runner System | $300 – $3,000 | High-end hot runner systems are needed for molds with multiple cavities, particularly for polycarbonate parts. |
| Profit | 10-20% | Varied based on the size of the factory, technical ability, and volume of the order. |
Note: Any quote that is more than 30% below the market price may indicate shortcuts, substandard materials, or overlooked critical steps.
1.2 Analysis of Mold Steel Types
Characteristics of different steel types:
| Steel Type | Characteristics | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| P20 | Good machinability, low cost | General housings, consumer products |
| 718 | High strength and wear resistance, easy to polish | Industrial parts, mid to high-end molds |
| H13 | High heat resistance, wear resistant | Precision parts, transparent components, hot runner molds |
| S136 / 1.2083 | High gloss, corrosion resistant | Optical components, medical transparent parts |
Tip: Request the steel batch number from the factory and consider third-party testing if necessary.
2. Injection Molding Unit Cost Breakdown
Formula Injection Molding Unit Cost = Material + machine setting-up + Labor Cost + Post-Processing + Packaging + Rework
2.1 plastic Material Cost
- Commodity vs. engineering plastics: ABS, PP, PC, PA66, POM, PC/ABS vary widely in price.
- High-performance materials: PC/ABS, PA66 GF30+ typically cost 3–5× standard PP.
- Colorants and pigments: Include extra costs for color masterbatch and transparent pigments.
2.2 machine setting up Cost
- Components: Machine electricity, machine wear, and time utilization.
- Complexity impact: Multi-sliders, hot runners, and complex geometries increase cycle time → higher unit cost.
- Mold quality: Poor mold design extends cycle time and raises costs.
2.3 Labor Costs
- Small factories: $2–$5 per hour
- Medium factories: $5–$10 per hour
- High-end (precision/optical): $10–$25 per hour
2.4 Post-Processing Costs
- Typical processes: Polishing, spraying/painting, screen printing, coating, assembly.
- Practice differences: Small factories may omit or outsource; high-end clients often require explicit line items in quotes.
2.5 Packaging Costs
- Standard vs. premium: Basic cardboard boxes vs. anti-static pallets.
- Customization: Client-branded or custom packaging incurs additional fees.
2.6 Rework Loss
- Acceptable defect rate: 1–5%
- High defect rate: 10%+ can directly double costs.
- Quality systems: Weak QC leads to hidden rework and scrap costs.
3. Hidden Cost Analysis
Overseas procurement frequently neglects several hidden costs, leading to actual total expenses that are 30% to 100% higher than the initial prices.
| Hidden Cost | Source | Avoidance Method |
|---|---|---|
| Differences Between Samples and Mass Production | Samples are made with high-quality materials or adjusted by engineers. | Conduct small batch trials to confirm production stability. |
| Mold Modification Fees | Unreasonable mold design leading to last-minute price increases by factories. | Implement Design for Manufacturability (DFM), mold flow analysis, and detailed contractual agreements. |
| Material Upgrades/Substitutions | Factories use recycled or lower-grade materials. | Clearly specify material brands, grades, and suppliers in the contract. |
| Logistics/Tariffs | Bulk exports incur additional shipping costs. | Estimate FOB, CIF, or DDP costs in advance. |
| Communication Delays | Lack of professional project management. | Appoint a project manager and establish clear reporting cycles. |
| Multiple Sample Revisions | Iterations from T1 to T3. | Clearly define the number of revisions and associated costs upfront. |
| Rework Costs | High defect rates. | Use quality control checklists and conduct small batch validations. |
Tip: The total cost of overseas procurement = Quoted Price + Hidden Costs. A comprehensive assessment is essential to determine the cost-effectiveness.
4. Supplier Quotation Comparison Template
Recommendation: Use a Three-Dimensional Scoring Method for Supplier Evaluation.
4.1 Template Example
| Supplier | Mold Cost Score (0–10) | Injection Unit Price Score (0–10) | Technical Capability Score (0–10) | Quality System Score (0–10) | Total Score | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supplier A | 8 | 7 | 9 | 8 | 32 | Has DFM, mold flow analysis, ISO certification |
| Supplier B | 6 | 9 | 5 | 6 | 26 | Low price but unknown mass production stability |
| Supplier C | 9 | 6 | 10 | 9 | 34 | Integrated mold factory, higher price |
Scoring Criteria:
- 0–3: Extremely Poor / Unacceptable
- 4–6: Average / Exercise Caution
- 7–8: Good / Collaborate
- 9–10: Excellent / Preferred Choice
Tip: This scoring method quickly eliminates low-quality, low-cost-effectiveness suppliers and allows for comparison of hidden costs.
Part 4: Quality Control and Production Stability in China Injection Molding
In previous sections, we discussed how to select the right injection molding suppliers in China and how to break down quotes to analyze hidden costs. However, even if a supplier possesses excellent technical capabilities, the absence of a comprehensive Quality Control (QC) system can lead to significant issues during mass production. This chapter will detail how to ensure stable and high-quality production through the utilization of systems such as Incoming Quality Control (IQC), In-Process Quality Control (IPQC), Final Quality Control (FQC), Outgoing Quality Control (OQC), First Article Inspection (FAI), and Capability Index (CPK).
1. Why Quality Control is More Critical than Supplier Selection
Choosing a reputable factory is just the first step; several risks still exist during mass production:
- Sample Quality vs. Production Variability: While samples may perform well, production batches can exhibit considerable variability.
- Raw Material Batch Differences: Variations in raw material batches can lead to inconsistencies in dimensions, color, or strength.
- Unstandardized Process Parameters: Lack of standardization in process parameters can result in shrinkage or warping of the final product.
- Inexperienced Operators: Insufficiently trained operators can lead to aesthetic defects in the products.
- Mold Wear and Tear: Over time, mold wear can cause critical dimensions to exceed acceptable tolerances.
Conclusion: The stability of mass production is a function of technical capability, QC processes, standardized operations, material management, and mold maintenance.
2. Common QC Processes in Chinese Injection Molding Factories
Chinese injection molding factories typically follow the processes outlined below, using English abbreviations commonly recognized in international procurement:
| QC Stage | Chinese Name | Core Objective |
|---|---|---|
| IQC | Incoming Quality Control | Inspection of raw materials, auxiliary materials, and purchased components |
| IPQC | In-Process Quality Control | Monitoring of critical dimensions and process parameters during production |
| FQC | Final Quality Control | Final inspection of finished products before shipment |
| OQC | Outgoing Quality Control | QC before shipping, confirming packaging, quantity, functionality, and appearance |
| FAI | First Article Inspection | Inspection of the first article to verify that molds and processes meet design requirements |
| CPK | Process Capability Index | Assessment of process capability, measuring batch stability |
This structured approach to quality control ensures that each stage of the production process is thoroughly monitored, enhancing the overall quality and reliability of the final products.
2.1 IQC — Incoming Quality Control
Objective: Ensure that raw materials and purchased components meet specified requirements.
Inspection Criteria:
- Material Specifications: Verify material grade, supplier, and batch number.
- Physical Properties: Assess color, gloss, and physical performance.
- Additive Proportions: Check the ratios of reinforcing materials or additives.
- Material Dimensions: Ensure particle integrity and measure dimensions.
- Testing: Conduct chemical composition or physical tests as necessary.
Tip: Poor quality raw materials can lead to production instability; IQC serves as the first line of defense against production failures.
2.2 IPQC — In-Process Quality Control
Objective: Identify issues during production to prevent batch rejection.
Key Focus Areas:
- Critical Dimension Checks: Inspect 1–5 pieces from each batch for key dimensions.
- Machine Parameter Monitoring: Track injection molding machine parameters such as temperature, pressure, holding time, and cooling duration.
- Mold Temperature and Cycle Monitoring: Regularly assess mold temperature and operational cycles.
- Operator Compliance: Verify that operators adhere to standard operating procedures for critical processes.
- Appearance Inspection: Look for defects such as warping, shrink marks, and bubbles.
Tip: IPQC can detect issues early in the production process, helping to avoid extensive rework.
2.3 FQC — Final Quality Control
Objective: Ensure that every product meets specifications before shipment.
Inspection Components:
- Appearance: Check for scratches, bubbles, and warping.
- Dimensional Accuracy: Measure critical dimensions using CMM or calipers.
- Functional Testing: Assess assembly, durability, torque, and other functional criteria.
- Packaging Inspection: Confirm quantity, labeling, and electrostatic protection.
Tip: FQC should not be limited to sampling; it must cover 100% of critical dimensions to guarantee product consistency for customers.
2.4 OQC — Outgoing Quality Control
Objective: Reconfirm that products align with customer requirements before shipment.
Inspection Points:
- Packing Quantity: Verify the number of items packed.
- Product Appearance and Functionality: Ensure that products meet visual and functional specifications.
- Packaging Integrity: Check that packaging is secure and intact.
- Shipping Documentation: Review documents such as Certificate of Compliance (COC), Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS), Packing List, and Test Report.
Tip: OQC acts as the final safeguard against customer complaints due to packaging or documentation errors during logistics.
2.5 FAI — First Article Inspection
Objective: Validate that molds, processes, and production parameters are correct.
Inspection Steps:
- Blueprint Comparison: Cross-reference with drawings or 3D files.
- Comprehensive Dimension Measurement: Measure all critical dimensions.
- Mold Life and Tolerance Check: Assess the mold’s lifespan and tolerances.
- Customer Approval: Samples must be signed off by the customer.
Tip: Skipping FAI can lead to significant production issues. Many low-cost factories bypass this step, which poses high risks.
2.6 CPK — Process Capability Index
Objective: Assess the stability of the production process and control critical dimension tolerances.
Common Metrics: Cp, Cpk
Applicable Scenarios: Hole positions, thickness, assembly dimensions
Statistical Analysis: Determine if process improvements are necessary through statistical analysis.
Mandatory for High-End Clients: Essential for industries such as automotive, medical, and optical.
Tip: Factories without CPK data cannot control dimensional variations during mass production.
3. Verifying Factory QC Capabilities
- Request QC Process Documentation: Ensure that proper documentation exists.
- Check for SOPs (Standard Operating Procedures): Confirm that SOPs are in place for each step.
- Assign Responsibilities: Verify that each stage has designated personnel responsible.
- Conduct On-Site or Video Audits: Perform inspections to assess practices.
- Review IQC Sample Testing: Evaluate the inspection process for incoming materials.
- Examine IPQC Sampling: Review the sampling procedures during production.
- Inspect FQC Records: Check documentation of final quality control.
- Observe OQC Packaging Processes: Assess how products are packaged for shipment.
- Request FAI Reports and Small Batch Data: Confirm the authenticity and completeness of first article inspection reports.
- Verify Batch Data with Statistical Records: Ensure that batch data is documented and analyzed.
- Monitor Trial Production: Conduct small batch production (50–200 pcs) with 5–10% sampling or 100% critical dimension checks.
- Validate Rework Rates and Standard Deviations: Analyze data to ensure quality control.
Tip: On-site audits combined with data verification are the golden combination for ensuring stable mass production in factories.
4. Complete Execution Process from Sample to Mass Production
4.1 Sample Phase
- T1: Verification of Factory Molding Capability
- Assess the factory’s ability to produce the desired parts.
- T2: Validation of Modified Samples
- Review and test any modifications made to the initial samples.
- Sample Confirmation Signature
- Obtain formal approval of the samples from relevant stakeholders.
- Small Batch Trial Production
- Produce a small batch of 50–200 pieces to evaluate production capabilities.
- Comprehensive Quality Checks
- Conduct thorough IQC (Incoming Quality Control), IPQC (In-Process Quality Control), and FQC (Final Quality Control) inspections.
- Confirmation of CPK and Yield Rates
- Analyze process capability (CPK) and yield rates to ensure quality standards are met.
4.2 Pre-Mass Production Preparation
- Mold Maintenance Status Confirmation
- Ensure molds are properly maintained and ready for production.
- Training for Key Process Operators
- Provide training to operators on critical processes to ensure consistency and quality.
- Standardization of Production Parameters
- Establish standardized parameters for temperature, pressure, cooling time, and ejection speed.
- Material Batch Confirmation
- Verify that the materials to be used in production meet specified requirements.
4.3 Mass Production Phase
- Sampling of Key Dimensions for Each Batch
- Perform random sampling of key dimensions to maintain quality control.
- Full FQC (Final Quality Control) Inspection
- Conduct a comprehensive inspection of all finished products.
- Final Review by OQC (Outgoing Quality Control)
- Perform a last check before shipment to ensure compliance with customer requirements.
- QC Data Recording and Archiving
- Document all quality control data for future reference and audits.
4.4 Long-Term Quality Monitoring
- Mold Life Management
- Plan for the lifespan of molds and schedule maintenance accordingly.
- Update Process Parameters
- Regularly review and update process parameters based on production data.
- Material Supplier Verification
- Continuously assess and validate suppliers to ensure quality consistency.
- Customer Feedback Collection
- Gather and analyze customer feedback to improve future production processes and product quality.
This structured approach ensures that each phase from sample development to mass production is executed meticulously, maintaining high standards of quality and efficiency throughout the process.
5. Practical Tools & Templates
A curated set of production-quality templates to make quality control measurable, consistent, and auditable. Here’s a structured overview of what’s included and how each template is used.
- QC Inspection Checklist (Dimensions, Appearance, Function)
- First Article Inspection (FAI) Template
- Batch Stability Record (Cpk Calculation)
- Rework and Defect Rate Analysis Sheet
Summary :Quality Control and Mass Production Stability
Quality control and mass production stability are critical determinants of whether a final product can successfully reach the market. The following key points outline the essential components of this process:
- Comprehensive Quality Control Process:
- The entire quality control spectrum, including Incoming Quality Control (IQC), In-Process Quality Control (IPQC), Final Quality Control (FQC), Outgoing Quality Control (OQC), First Article Inspection (FAI), and Process Capability Index (CPK), must be rigorously implemented without exception.
- Importance of Small Batch Trials:
- Conducting small batch trials is crucial for validating mass production capabilities. These trials help assess the production process and identify potential issues before full-scale manufacturing.
- Data-Driven Monitoring and Recording:
- Implementing data-driven monitoring and recording systems can significantly reduce risks over the long term. This approach allows for real-time tracking of production metrics and quick identification of anomalies.
- Maintenance of Molds and Material Management:
- Regular maintenance of molds and effective management of materials are equally important. These practices ensure that production equipment operates efficiently and that the quality of materials used meets the required standards.
- Significance of Quality Control Capabilities:
- The quality control capabilities of a factory are more critical than merely offering low prices. A robust quality control system ensures product consistency and reliability, ultimately leading to higher customer satisfaction and trust.
By adhering to these principles, manufacturers can enhance their quality assurance processes, thereby ensuring that their products are market-ready and meet consumer expectations.
Part 5 — China injectionmolding:Long-Term Collaboration
In the previous four sections, we have thoroughly discussed:
- Caution in Choosing Chinese Suppliers (Part 1):
- The importance of careful consideration when selecting suppliers from China to mitigate risks and ensure quality.
- Systematic Evaluation of Supplier Capabilities (Part 2):
- A structured approach for assessing the capabilities of potential suppliers, focusing on their strengths and weaknesses.
- Analysis of Mold Costs, Injection Pricing, and Hidden Expenses (Part 3):
- A detailed examination of the costs associated with molds and injection molding, including often-overlooked expenses that can impact overall budgeting.
- Quality Control Processes and Mass Production Stability (Part 4):
- The critical role of quality control in ensuring stable mass production and the factors that contribute to product reliability.
The next emphasis is on strategies for converting outstanding suppliers into dependable long-term partners. This transformation is essential for establishing sustained competitive advantage in the market.
1.The Value of Long-Term Collaboration
Choosing a supplier is not merely a transactional decision; it is a strategic long-term commitment:
- Cost Reduction: Long-term partnerships allow for negotiations on better pricing and payment terms.
- Quality Stability: Suppliers become familiar with your products and processes over time, leading to lower rework rates.
- Increased Responsiveness: Urgent orders, mold modifications, and special material requests can be handled swiftly.
- Supply Chain Risk Mitigation: Establishing trust reduces the risk of critical component shortages.
- Innovation Promotion: Suppliers can actively participate in design optimization, material selection, and process improvements.
Tip: The lowest initial cost does not equate to the lowest total cost. The value of long-term collaboration often outweighs the benefits of a one-time low price.
2. Key Elements of Supplier Management
2.1 Contract and Agreement Management
- Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA):
- Ensure confidentiality for mold designs, formulations, and process documents.
- Protect your intellectual property.
- Mold Ownership Clauses:
- Clearly define mold ownership.
- Outline maintenance, depreciation, and obsolescence handling.
- Delivery Terms (FOB / CIF / DDP):
- Confirm logistics responsibilities.
- Avoid disputes over hidden shipping costs.
- Quality Terms:
- Specify QC standards and first article inspection requirements in the contract.
- Include clauses on defect rates, rework costs, and compensation.
- Payment Terms:
- Implement phased payments: T0 (contract signing), T1 (mold completion), and pre-mass production.
- Avoid full upfront payments to minimize risk.
2.2 KPI and Performance Management
To ensure effective long-term collaboration, it is essential to quantify supplier performance through Key Performance Indicators (KPIs):
| KPI Indicator | Description | Measurement Method |
|---|---|---|
| On-Time Delivery Rate | Timeliness of deliveries | Actual delivery date vs. scheduled delivery date |
| Yield Rate | First-pass product quality | Rate of rework and inspection results |
| Technical Response | Speed of resolving engineering issues | Average response time |
| Communication Efficiency | Speed of email/WeChat/Skype responses | Average response time |
| Quality Complaints | Issues identified by customers or internally | Number of complaints per 1000 pieces |
Tip: Conduct regular KPI evaluations (quarterly or biannually) for suppliers and link the results to pricing and contract adjustments.
2.3 Risk Sharing Mechanism
Mold Maintenance and Damage
- Responsibility: The factory is responsible for significant damages beyond normal wear and tear of the molds.
- Support: You will provide essential materials or process guidance.
Material Fluctuations
- Agreement: The contract should stipulate material upgrades and alternative options.
- Cost Sharing: Reasonable cost-sharing for fluctuations in material prices.
Urgent Orders
- Priority Terms: Establish expedited fees or priority production terms.
- Clarified Responsibilities: Clearly define the responsibilities of both parties.
Tip: A risk-sharing mechanism aligns the interests of both parties, enhancing the stability of long-term collaboration.
3. Best Practices for Overseas Procurement and Supplier Communication
3.1 Project Management
- Designate a Project Manager (PM): Assign a PM to oversee the entire process.
- Responsibilities: The PM is responsible for communication, tracking progress, and document archiving.
- Milestones: Establish key milestones for each critical phase (design, mold, samples, mass production).
3.2 Maintaining Factory Relationships
- Regular Meetings: Schedule periodic video or on-site meetings.
- Participation: Involve suppliers in mold and sample reviews.
- Timely Feedback: Provide prompt feedback and recognition to suppliers.
- Long-term Collaboration Incentives: Implement rewards such as priority orders and bulk discounts.
3.3 Collaboration on Processes and Design
- Share DFMEA / DFM Reports: Exchange Design Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (DFMEA) and Design for Manufacturing (DFM) reports.
- Propose Improvements: Encourage factories to suggest feasible improvements.
- Validate Improvements: Test improvements through samples or small batch production.
Tip: Establish a transparent, two-way communication mechanism to avoid information silos and misunderstandings.
4. Continuous Supply Chain Optimization
Long-term collaboration encompasses not just procurement contracts but also the optimization of supply chain capabilities:
- Material Supply Chain Optimization:
- Collaborate with factories and material suppliers to secure stable sources of raw materials.
- Implement unified batch management to reduce variability.
- Mold Maintenance Plan:
- Schedule regular maintenance, lubrication, and cleaning.
- Track mold lifespan and predict replacement cycles.
- Production Capacity Upgrades:
- Negotiate production schedules during peak periods.
- Focus on equipment upgrades or expansion capabilities.
- Quality Data Analysis:
- Establish a Quality Control (QC) database.
- Regularly analyze dimensional tolerances, rework rates, and customer complaints.
- Drive improvements through data analysis.
5. Summary
The core of a long-term collaboration strategy includes:
- Contracts and Intellectual Property Protection: Utilize Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDA), mold ownership clauses, and quality terms.
- KPI and Performance Management: Quantify supplier performance and establish reward and penalty mechanisms.
- Risk Sharing Mechanism: Address molds, materials, and urgent orders.
- Communication and Project Management: Implement PM systems, regular reviews, and transparent feedback.
- Continuous Supply Chain Optimization: Focus on material management, mold maintenance, production capacity upgrades, and data analysis.
Tip: Long-term collaboration is defined by price, quality, speed, and trust; short-term low prices cannot replace the advantages of a stable supply chain.