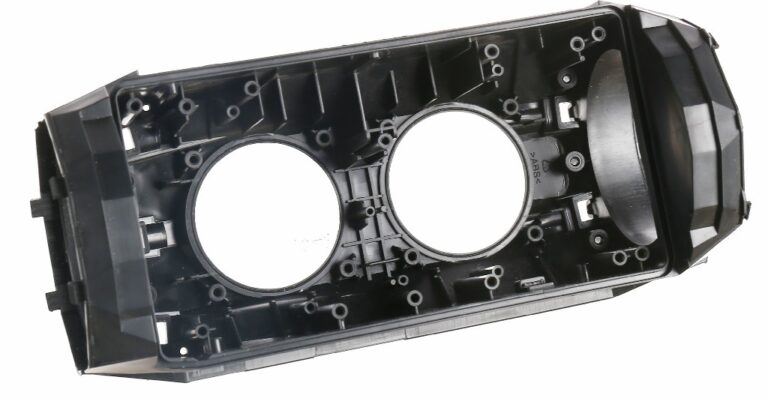
ABS-Spritzgießdienstleistungen aus China: Schnelle Lieferung und kleiner Auftrag verfügbar
Sind Sie auf der Suche nach einem ABS-Spritzgießen Hersteller und Designer - der die Rentabilität Ihres Unternehmens verbessern wird? Suchen Sie nicht weiter als Topworks Plastic mold: Ein chinesisches Spritzgussunternehmen, das kundenspezifischen ABS-Kunststoff-Spritzguss mit vollem Service anbietet.
One-Stop ABS Injection Molding in China — Time-Controlled, Quality-Stable, Cost-Predictable
Topworks provides a one-stop ABS injection molding service for OEMs and brand owners — covering DFM, tooling, sampling, mass production, and quality control under one responsible team.
Best results with: STEP/IGES + ABS grade (e.g., FR / heat-resistant) + annual volume + cosmetic requirements + CTQ dimensions.

One supplier accountable end-to-end
No hand-offs. No “tooling vendor vs molding vendor” blame. One system controlling output.
Fewer surprises, fewer re-cuts
DFM before steel + structured sampling reduces trial-and-error and protects schedule.
Cycle stability + scrap control
The lowest quote rarely equals the lowest total cost. Stable production wins long runs.
Why Buyers Prefer One-Stop ABS Injection Molding
In real sourcing, ABS projects fail more often due to fragmented responsibility than material choice. When mold, sampling, and production are managed by different parties, delays and quality disputes become common.
One-stop ABS injection molding means: one accountable supplier, one engineering logic from design to production, one coordinated timeline, and one cost structure aligned with mass production reality.
What “One-Stop” Means at Topworks
1) DFM-first review
Wall thickness, ribs/bosses, gate location, draft, cosmetic surfaces, CTQ/tolerance zones.
2) Production-ready tooling
Balanced cooling + venting designed for ABS stability and repeatability, not just samples.
3) Sampling + validation
Trial plan, FAI measurement, golden sample definition, process window set for production.
4) Mass production
Process monitoring, cosmetic control, dimensional audits, packaging and shipping support.
Time Control: Predictability Beats “Fast Promises”
Buyers rarely only ask “how fast.” They want to know whether the program stays on schedule. Time is protected by early DFM decisions, fewer sampling rounds, and faster issue resolution within one team.
- DFM before cutting steel reduces rework risk
- Clear sampling targets avoid endless iterations
- One supplier resolves issues without hand-off delays
Quality: Stable Production, Not “Perfect Samples”
Mass production is where weak tooling/process systems fail. ABS risks are controlled by design + cooling + process window discipline.
- Sink marks over ribs/bosses
- Warpage causing assembly failure
- Burn marks / short shots from poor venting
- Cosmetic inconsistency across shifts/batches
- Dimensional drift over long runs
Cost Control: Total Cost, Not Just Unit Price
Experienced buyers evaluate total cost of ownership (TCO): scrap, rework, downtime, and cycle stability. Low tooling cost can create high production cost when cooling, venting, and process windows are not engineered for long runs.
- Cycle time stability reduces unit cost at scale
- Lower scrap rate protects delivery and budget
- Fewer mold modifications reduce hidden costs
- Stable output reduces firefighting and line stoppages
ABS Defect Controls (Topworks Approach)
| Defekt | Buyer Risk | Common Root Cause | Topworks Control |
|---|---|---|---|
| Einfallstellen | Cosmetic rejection | Thick ribs/bosses, poor packing balance | Rib ratio optimization + boss coring + gate/pack tuning + cooling balance |
| Verzug | Assembly failure | Cooling imbalance, residual stress | Cooling redesign (baffles/bubblers) + gate balance + validated process window |
| Burn marks | Appearance defect | Trapped gas, insufficient venting | Venting/overflow strategy + staged filling speed + temperature control |
| Kurze Schüsse | Scrap spikes | Flow restriction, poor venting | Gate sizing + venting + flow path optimization |
ABS Case Studies (Before / After)
Replace the images below with your real photos (recommended: one split image per case, left=before, right=after). The numbers are realistic-style examples; update them to match your projects.
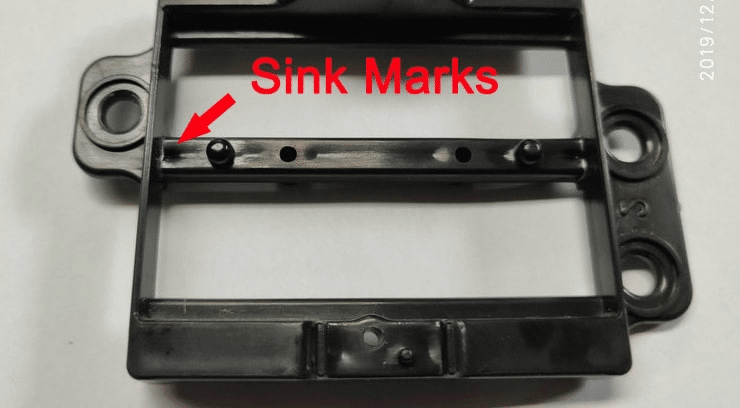
Case 1: Cosmetic ABS Housing — Sink Marks
- Visible sink over ribs and bosses
- Cosmetic rejection at incoming QC
- Rib thickness optimized; bosses cored
- Packing profile stabilized; gate balance improved
- Cooling tuned to reduce local hot spots
Case 2: ABS Structural Bracket — Warpage
- Twist after ejection caused misalignment
- Dimensional drift between cavities
- Cooling redesigned (baffles) to balance temperature
- Gate location tuned to reduce stress concentration
- Hold/pack window validated for production

Case 3: Thin-Wall ABS Bezel — Burn Marks
- Burn marks near end-of-fill
- Inconsistent appearance across shifts
- Added vents/overflow at end-of-fill
- Staged filling speed to reduce shear heating
- Standardized start-up parameters for repeatability

Who This Service Is For
- OEM manufacturers and brand owners
- Procurement teams sourcing from China
- Engineering teams needing stable production, not just samples
- Programs where cosmetic quality and assembly fit matter
Who This Is NOT For
- Buyers choosing suppliers only by lowest tooling price
- Projects without clear requirements or CTQs
- One-off prototype buyers with no production plan
Filtering price-only projects protects delivery, quality, and engineering focus for serious programs.
FAQs — ABS Injection Molding (Topworks)
What do you need to quote ABS injection molding accurately?
How do you control sink marks and warpage in ABS?
Can you reduce total cost, not just tooling cost?
Do you support one-stop service from tooling to shipment?
Helpful Resources (Internal)
Use these links to help buyers evaluate cost, process, defects, and sourcing risk.
Ready to Start Your ABS Project?
Send CAD + requirements to Topworks for a quote-ready DFM review and a production-focused ABS molding plan.

ABS Injection Molding FAQ
Top 10 essential questions about ABS plastic injection molding
ABS injection molding is a manufacturing process that uses injection molding machines to produce parts from Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) plastic resin. The process involves heating ABS pellets to 200-250°C until molten, then injecting the material under high pressure (10,000-20,000 psi) into a precision mold cavity where it cools and solidifies into the desired shape.
ABS is one of the most popular thermoplastics for injection molding due to its excellent balance of strength, impact resistance, surface finish quality, and cost-effectiveness. It’s widely used in automotive components, consumer electronics, toys, appliances, and industrial parts.
Impact Resistance: Excellent toughness even at low temperatures (-20°C to -40°C), making it ideal for durable products
Mechanical Strength: Tensile strength of 40-50 MPa with good rigidity and dimensional stability
Surface Quality: Superior surface finish with high gloss potential, easy to paint, plate, or print
Heat Resistance: Service temperature range of -20°C to 80°C, with heat deflection temperature around 95-105°C
Chemical Resistance: Good resistance to acids, alkalis, and most chemicals, but vulnerable to acetone and strong solvents
Processability: Excellent flow characteristics and low shrinkage rate (0.4-0.7%), enabling precise tolerances
Automotive: Dashboard components, interior trim, door panels, mirror housings, wheel covers, grilles
Electronics: Computer keyboards, monitor housings, printer cases, phone casings, power tool housings
Consumer Goods: Toys (LEGO bricks), sporting goods, luggage, kitchen appliances, vacuum cleaner parts
Medizinische Geräte: Non-implantable medical equipment housings, diagnostic device casings
Industrial: Protective equipment, electrical enclosures, pipe fittings, safety helmets
Drying: Essential – dry ABS at 80-90°C for 2-4 hours (moisture content should be below 0.1%)
Barrel Temperature: Rear zone 180-200°C, middle zone 200-220°C, front zone 220-240°C, nozzle 220-250°C
Mold Temperature: 50-80°C (higher temperatures improve surface finish but increase cycle time)
Injection Pressure: 80-140 MPa (10,000-20,000 psi) depending on part complexity
Injection Speed: Medium to high speed for best results, avoiding very slow speeds that cause flow marks
Cooling Time: Typically 20-90 seconds depending on wall thickness (calculate approximately 1 second per 1mm of wall thickness)
Material Cost: ABS resin costs $1.50-$3.50 per kg depending on grade and quantity
Tooling/Mold Cost:
• Simple single-cavity mold: $3,000-$8,000
• Medium complexity (2-4 cavity): $12,000-$25,000
• High-volume multi-cavity: $35,000-$80,000+
Per-Part Cost: For volume production (10,000+ parts): $0.50-$5.00 per part depending on size and complexity
Setup Costs: Typical setup/trial run: $500-$2,000
Overall costs decrease significantly with volume – parts can cost $10-$20 each for low volumes (100-500) but drop to under $1 for high volumes (100,000+).
Flow Marks/Weld Lines: Increase mold temperature to 70-80°C, increase injection speed, optimize gate location
Sink Marks: Reduce wall thickness variations, increase holding pressure and time, ensure adequate cooling
Warping: Reduce mold temperature difference between core and cavity, ensure uniform wall thickness, optimize cooling channels
Burn Marks: Reduce injection speed, lower barrel temperature, improve venting, reduce clamp force
Silver Streaks/Splay: Dry material thoroughly (most common cause), reduce barrel temperature, check for contamination
Short Shots: Increase injection pressure and speed, raise melt temperature, improve venting, check for cold gates
Yes, ABS is highly recyclable and commonly reprocessed in injection molding operations:
Regrind Usage: Post-industrial ABS scrap (sprues, runners, rejected parts) can be ground and reused at 10-25% blend with virgin material without significant property loss
Quality Considerations: Each reprocessing cycle slightly degrades mechanical properties due to polymer chain breakdown. Limit reprocessing to 3-5 cycles for critical applications
Best Practices: Keep regrind clean and dry, avoid mixing different ABS grades or colors, test mechanical properties when using >15% regrind
Post-Consumer Recycling: ABS from electronics and automotive parts can be recycled, though sorting and cleaning are critical for quality
Using recycled ABS reduces costs by 20-40% and supports sustainability goals while maintaining acceptable part quality for many applications.
Wanddicke: Maintain uniform thickness of 1.2-3.5mm; avoid variations >25% to prevent sink marks and warping
Entwurfswinkel: Minimum 0.5-1° per side for smooth ejection; textured surfaces require 1-3° additional draft
Ribs and Bosses: Rib thickness should be 50-60% of wall thickness, boss wall thickness 50% of nominal wall
Corner Radii: Use minimum radius of 0.5mm for inside corners, 1.5mm for outside corners to reduce stress concentration
Hinterschneidungen: Minimize or avoid; if necessary, design for side-action cores or collapsible cores
Gate Location: Place gates in non-visible areas; use multiple gates for large parts to reduce fill time and pressure
Toleranzen: ABS can achieve ±0.1-0.2mm for dimensions under 50mm with proper mold design
ABS vs. Polypropylene (PP): ABS offers better rigidity, surface finish, and dimensional stability; PP is more flexible, chemical resistant, and cheaper
ABS vs. Polycarbonate (PC): PC has higher impact strength and heat resistance (up to 120°C); ABS is easier to process, cheaper, and has better surface finish
ABS vs. Nylon (PA): Nylon offers superior mechanical strength and wear resistance; ABS provides better dimensional stability and surface quality at lower cost
ABS vs. HIPS: ABS has significantly better impact resistance and mechanical properties; HIPS is cheaper and easier to thermoform
ABS vs. PC/ABS Blend: PC/ABS combines advantages of both, offering better heat and impact resistance than pure ABS at 20-30% higher cost
ISO 9001: General quality management system for manufacturing processes and consistency
ISO 2580: Specific standard for ABS molding materials, defining properties and test methods
ASTM D4673: Standard classification for ABS materials by physical and mechanical properties
UL 94: Flammability testing for ABS parts in electrical and electronic applications
RoHS/REACH: Compliance for restricted substances, especially for electronics and automotive applications
FDA Approval: Required for food-contact applications using FDA-compliant ABS grades
Automotive Standards: IATF 16949 for automotive component suppliers, plus OEM-specific requirements
Quality control should include dimensional inspection, visual inspection, mechanical testing (tensile, impact), and environmental testing (UV, thermal cycling) based on application requirements.